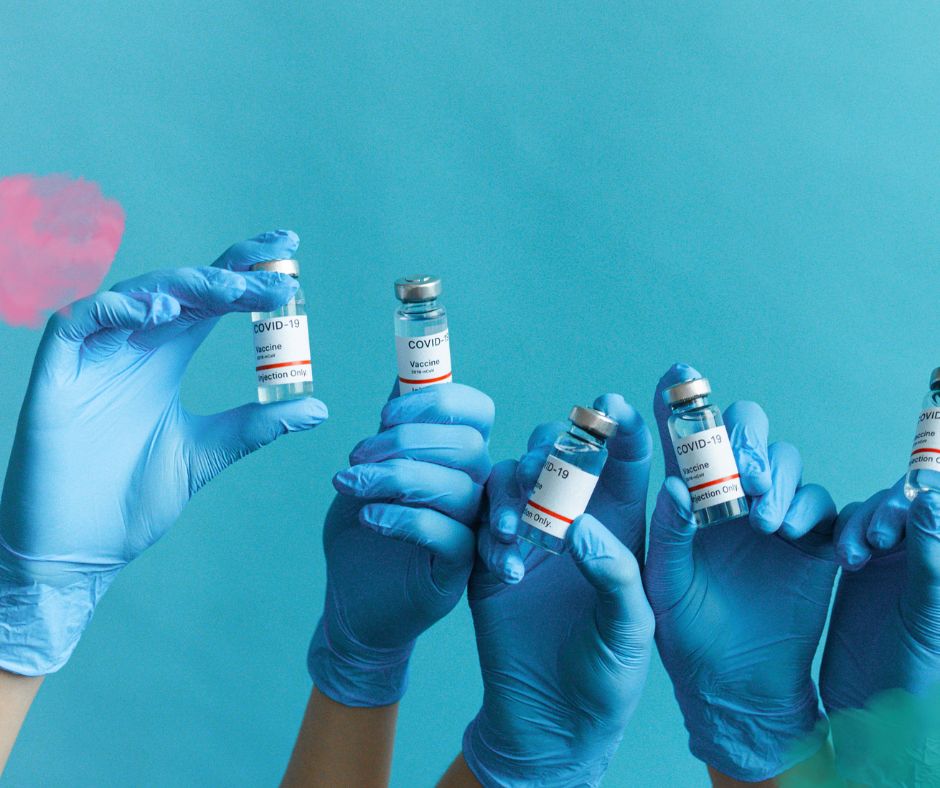
The first time I heard of booster shots was in my early years of University. I needed to travel to an Asian country and was told I would have to get a booster for measles mumps and rubella (MMR). I was young then and didn’t ask too many questions, I just went ahead and got my booster shot so I wouldn’t be denied the opportunity to travel.
Booster doses were being promoted as far back as 1964. Many of us have being getting booster shots unaware. A very common example is the Tetanus toxoid (TT) shot. Have you ever being injured by a nail, wood or foreign object? Many of us might administer first aid at home and will be in favour of getting a TT shot afterwards. It is the most common and widely accepted example of a booster shot. Childhood vaccination schedules also work with booster shots gotten in monthly, bi or tri monthly intervals.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many chose not to get their COVID vaccines and many others did get their shots. Now in the post COVID era, booster shots are being encouraged in some countries.


What is a booster shot?
A booster shot is ‘ an additional dose of a vaccine after an earlier (primer or main) dose’. The first dose of any vaccine is the primer. It’s the first introduction of a foreign genetic material into the body. Upon contact with our body’s defense cells, these cells can then produce antibodies to defend against future infections.
The body fights off infections through white blood cells. These white blood cells are of a number of types. Those responsible for carrying out the post immunization process are memory T cells and B cells. The T cells are responsible for recognizing the invading germs while the B cells produce antibodies to ward off the invasion.
Both of these cells have an important role in protecting against severe disease but are more difficult to measure compared to the antibodies produced by B cells. The best way to determine if one needs a booster dose is by measurement of the level of antibodies against the specific disease, months or years after the primary dose was given.
The best way to determine if one needs a booster dose is by measurement of the level of antibodies against the specific disease, months or years after the primary dose was given.
Boosters are given to make sure that the body has an optimum level of these antibodies.
Some vaccines offer long lasting immunity, while others offer immunity for a shorter period. For example, Current COVID vaccines offer immunity which wanes after 4-6 months necessitating the need for a booster dose.
Now in some persons, immune-compromised persons, cancer patients, elderly patients, these antibodies can wane much faster. Hence, in the example of COVID, persons with immunocompromised systems are urged to get the COVID booster in 2-3 months after their last dose
Booster doses in case of flu shots are necessary to update one’s immunity due to emerging virus variants.
What’s up with COVID boosters?
Currently the issuance of COVID-19 booster doses is questionable as extensive research has not yet been carried to show how long these antibodies can last following an infection or vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine. Due to the existence of many COVID-19 variants though, a booster could be indicated if proven to offer added protection from other variants.
The Recommendation in Australia
Australia’s inflexible rules during COVID prevented Djokovic from participating in the Australia Open, well they haven’t relented in the post covid-era. And it’s very interesting to note that they have research to back up their policies.
Booster doses are currently encouraged in Australia due to the emergence and spread of multiple new omicron variants. These booster doses are administered in order to prevent severe disease from COVID, although (contrastingly) it is acknowledged that these newer variants do not cause severe disease[3]
ATAGI recommends these booster doses for mainly three sets of persons; Patients with comorbid diseases, Adults aged 65 years and above and adults aged 18-65 without any health risk factors but with more than 6 months gap since their last COVID infection.
What is the WHO recommendation for COVID booster shots?
The World Health Organization recommends COVID-19 boosters for those whose immune systems are compromised and for persons aged 60 and above.
Having a vaccine card is an easy and effective way of knowing when and where you might need a booster shot. The guidelines are to follow your country’s recommendation for taking vaccines and booster shots if recommended. One who is travelling to a new country, should also pay attention to their recommended vaccine guidelines.
Vaccination is preventive medicine, it has saved more lives than any other medical invention in the world. It’s a cheap price to pay to save up on any future troubles.
The prediction though is that like Influenza shots, COVID 19 boosters are here to stay.
What is the recommendation for COVID boosters in your country?
REFERENCES
- Canadian Medical Association Journal CMAJ. 2021 Sep 7; 193(35): E1400-E1401. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1095959
- New Sci. 2021 May 15; 250(3334): 8-9. 2021 May 14. doi: 10.1016/S0262-4079(21)00808-3
- World Health Organization WHO April 2022. COVID-19 Advice for the Public
- https://www.health.gov.au/news/